The Multimedia module stores all multimedia resources used throughout EMu. It complies with the Dublin Core Metadata Standard and the complete Dublin Core attribute set can be recorded for each multimedia resource.
Records in almost every module can include multimedia resources. There is no limit to the number of multimedia resources that can be included with a record, nor the type of those resources.
Note: The Multimedia repository can also be used to store resources that aren't necessarily related directly to a collection record (e.g. marketing collateral, minutes of meetings, planning papers).
A Microsoft Word research document about an object in the Catalogue and a digital image of the object can be stored in the Multimedia module and associated with the object's record in the Catalogue. Similarly, a copy of a loan document in Microsoft Word format, and a scanned image of the document signatures, for verification purposes, can be associated directly with a loan. When the object or loan information is viewed, all associated multimedia resources are also available.
Not only can EMu store any multimedia resource, it has the ability to show / play more than 100 image, video and audio formats.
A Multimedia record holds information such as:
- Type of resource (image, audio, video, etc.)
- Format of the resource (GIF, JPEG, AU, WAV, MPEG, etc.)
- Source
- Description
- Creators and other contributors
- Restrictions on the use of the resource
Derivative versions of an image can be generated automatically to satisfy different requirements. For instance, a thumbnail JPEG can be generated for browsing, an 800x600 PNG image for publication on the web, whilst maintaining the image in its original format and resolution.
EMu supports not only basic multimedia types supported (images, audio and video), but complex objects also (Word documents, Excel spreadsheets, etc.). Its multimedia support is also extensible: an external viewer can be associated with a multimedia type so that adding a new media format is as easy as installing the appropriate viewing application on your workstation.
If the multimedia resource is textual (and a suitable viewer is defined), the content of the document is fully indexed, thus enabling full text retrieval (see How to search attached documents for details).
When you access or view a multimedia resource it is downloaded and cached on your local PC. Multimedia resources can be viewed within EMu (on a module's Multimedia tab or in the Multimedia module itself) or via an external viewer: external viewers must be registered on your local PC to play the required multimedia formats.
Tip: EMu's Multimedia repository can be extended to a full blown Digital Asset Management system with the browser-based Axiell DAMS.
Note: As every institution is able to customize EMu to suit its requirements, there are many different versions of EMu. Even where institutions have the same modules, the tabs included in each instance of the module may be different; and even where institutions have tabs with the same name, the fields on those tabs may be different. For that reason this section only provides a general description of modules.
Tip: See below for a description of the purpose of fields.
|
Tab |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Multimedia |
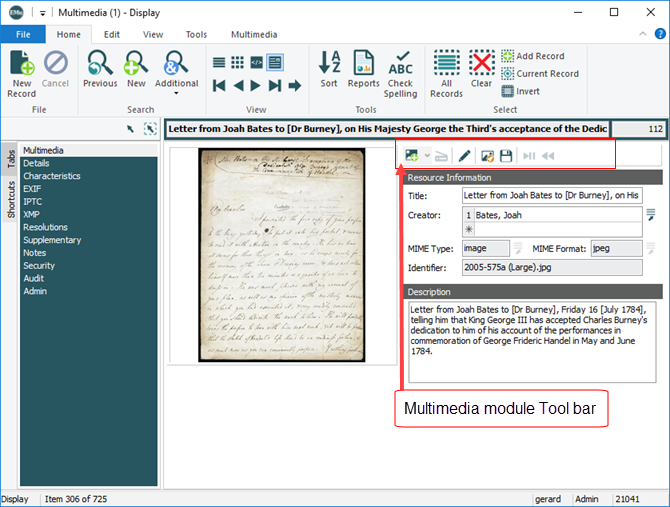
This tab records:
See Multimedia module commands for details about commands available on the Multimedia tab of the Ribbon, and the Multimedia module Toolbar. |
|
Details
|
Holds details about the multimedia, including:
|
|
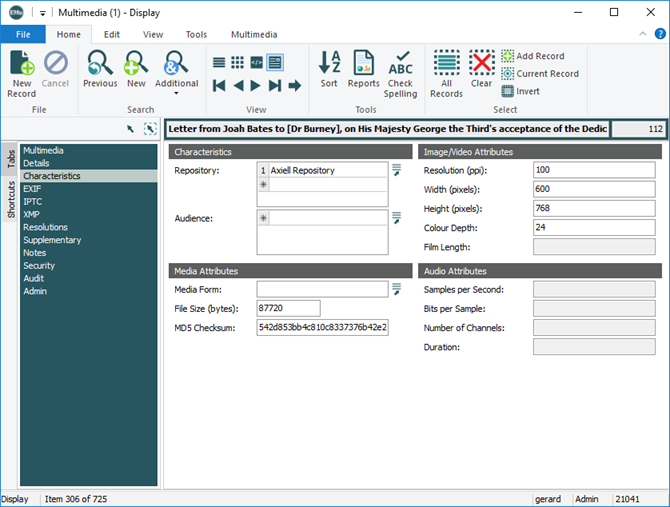
Characteristics
|
This tab records characteristics of the current multimedia, including:
|
|
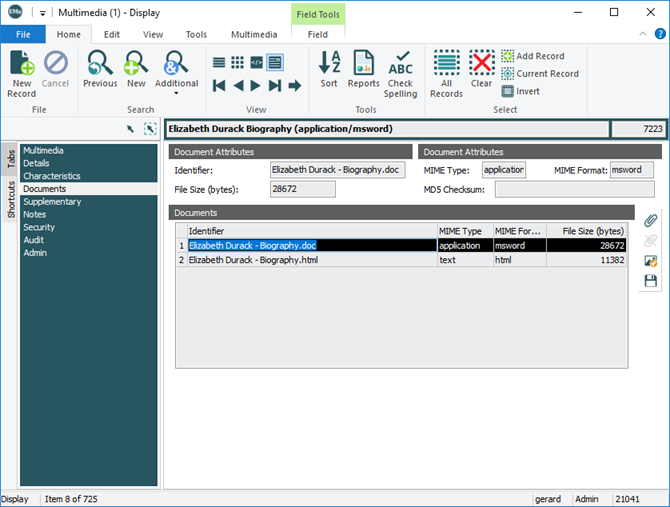
Documents
|
The Documents tab displays when any other resource than an image is added to the Multimedia module (audio, video, document, etc.). It records:
Media can be added, deleted, modified, viewed and saved to the Documents table. See also:
|
|
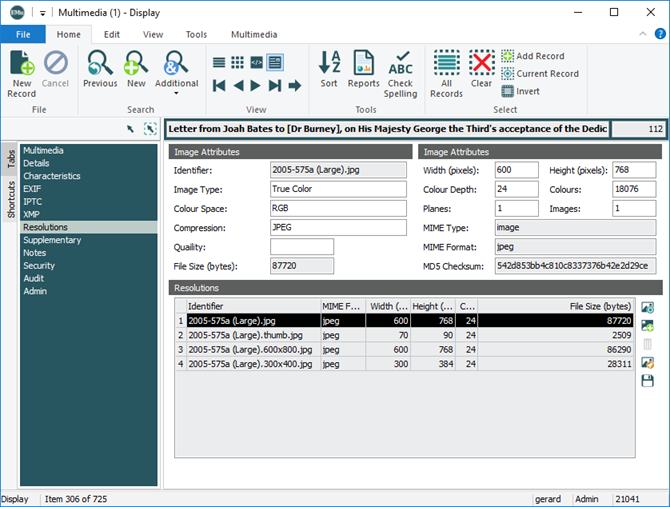
Resolutions
|
The Resolutions tab displays when an image is added to the Multimedia module. Details include:
Media can be added, deleted, modified, viewed and saved to the Resolutions table. See also:
|
|
Supplementary |
Supplementary media provides a mechanism for storing associated media resources along with a master resource in the same Multimedia record. The bottom half of the tab consists of a Supplementary table that lists all supplementary media. The set of fields above the table display data about the media currently selected in the Supplementary table. Only the Usage, Notes, Width and Height fields may be altered. All other fields are calculated by EMu automatically and cannot be modified. Note: Identifier must be unique in the Supplementary table for the current record. Media can be added, deleted, modified, viewed and saved to the Supplementary table. See also:
|
|
EXIF |
When an image is added to the Multimedia module EXIF metadata is extracted from the source file and added to this tab (EXIF supports jpeg and tiff formats). This tab is currently read-only; data on this tab can be used in a search and included in a report. See Supported formats and metadata for more details. |
|
IPTC |
When an image is added to the Multimedia module IPTC metadata is extracted from the source file and added to this tab (IPTC supports jpeg, tiff, pict, ps and psd formats). This tab is currently read-only; data on this tab can be used in a search and included in a report. See Supported formats and metadata for more details. |
|
XMP |
When an image is added to the Multimedia module XMP metadata is extracted from the source file and added to this tab (XMP supports jpeg and tiff image formats). This tab is currently read-only; data on this tab can be used in a search and included in a report. See Supported formats and metadata for more details. |
|
Annotations1 |
Read-only tab holding details about annotations and line drawings made to an image in Sapphire. This information is used to reload annotations / drawings when the image is viewed in Sapphire. For every image that is modified with the Sapphire Annotate or Draw tool, you will find two Multimedia records:
The Annotations tab in the record with the original image includes read-only details about all annotations and lines added to the image. This information is used to reload annotations / drawings when the image is viewed in Sapphire. An annotation has a Type of text; a line drawn with the Draw tool has a Type of draw: Details about an annotation include the text; coordinates of an annotation ( For a line drawn with the Draw tool, the Coordinates list is a group of points defining the line: Again, More details here. |
|
Notes |
See Notes tab for details. |
|
Security |
See Security tab for details. |
|
Audit |
See Audit tab for details. |
|
Admin |
See Admin tab for details. |
|
Field Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Identifier |
The file name given to the media on the EMu server. When adding new media the name of the file being imported is used as the default identifier. An identifier may consist of any characters, including spaces, except for:
|
|
Width (pixels) |
If the media is an image, the width in pixels is calculated automatically and stored. For other types of media that have a width in pixels (e.g. video) the value may be entered manually. |
|
Height (pixels) |
If the media is an image, the height in pixels is calculated automatically and stored. For other types of media that have a height in pixels (e.g. video) the value may be entered manually. |
|
MIME Type |
The type of the media. EMu calculates the MIME Type automatically and adds the value to this field. The MIME Type is a high level term describing the overall category into which the media belongs. Example values are: image, video, audio, application, etc. MIME Types available in EMu are defined by RFC 2046. |
|
MIME Format |
The format used to store the media. The value is used to determine how the media should be decoded for viewing, playing, etc. For each MIME Type there is a wide range of available formats. As with the MIME Type, EMu calculates the MIME Format automatically and adds the value to this field. |
|
MD5 Checksum |
When a media file is ingested by EMu an MD5 Checksum is automatically computed on the file, producing a 32 character hexadecimal number similar to: As virtually any change to a file causes the checksum to change, it can be used to verify the integrity of files: any difference between the checksum generated at ingest with the current checksum indicates a change in the file. MD5 checksum validation at each step in the automated process, so that network errors and any other unintended file corruptions can be automatically resolved. |
|
File Size (bytes) |
The size of the file in bytes. EMu calculates the size of the media automatically and adds the value to this field. The value may be used to determine download times, storage requirements, etc. |
|
Usage |
A list of values outlining what the media may be used for. The usage field allows media to be searched for based on its purpose. A Lookup List is provided to allow some vocabulary control over the available values. |
|
Notes |
An area where notes about the media may be stored. The notes may describe what the media contains, or it may be information that is displayed along with the media when displayed on a website (e.g. copyright information, a credit line, a textual label). |